STD INFO
ARE YOU AT RISK?
Infectious diseases seem to come and go, sometimes causing scary outbreaks, while other times seeming to disappear. But some infectious pathogens are always with us, lurking just below the surface of society.
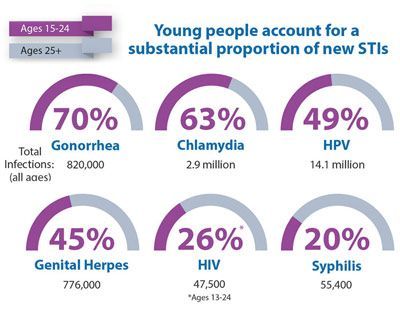
Sexually transmitted diseases are one major group of diseases that make for ongoing hidden epidemics: In the United States alone, there are nearly 20 million cases of new sexually transmitted infections yearly, from just eight viruses and bacteria, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
STDs are infections spread by sexual contact with skin, genitals, mouth, rectum, or body fluids. Although some STDs can be treated, others cannot. People with an STD may not know they have it.1 According to the Centers for Disease Control, in the United States, 1 out of 4 women between the ages of 14 and 19 is infected with at least one STD.
More more statistical information, please visit this site.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD’s) pose a serious risk to future reproductive and overall health, especially if left untreated. People who have an STD are at least 2 to 5 times more likely to contract HIV, the virus which leads to AIDS.2
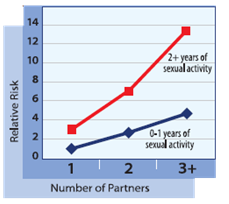
More than 1 in 3 female teens who have had sex have an STD.3 As your number of partners and sexual encounters increases, your risk of contracting an STD increases dramatically.
NOTE: NOTIFY ALL SEX PARTNERS THAT YOU HAVE AN STD SO THEY CAN BE TESTED AND TREATED. YOU SHOULD BE RE-TESTED FOR STDS 3-4 MONTHS AFTER FINISHING TREATMENT.
WHAT IS YOUR STD RISK RATIO?
Most STD’s go un-diagnosed because symptoms are not recognized or are very mild. An infected individual can share an STD with their partner before ever realizing they have one. Because some STD’s are asymptomatic; meaning they show no signs or symptoms of disease, it’s important to be tested. Life Choices Women’s Center will soon be offering STI/STD testing (Fall 2017). Please give us a call to receive more information.
PREVALENT STDS
CHLAMYDIA | GONORRHEA | BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS (BV) | HEPATITIS B | HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS | HIV/AIDS | SYPHILIS | TRICHOMONIASIS
CHLAMYDIA
Definition: A common sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium, Chlamydia trachomatis, which can damage a woman’s reproductive organs.
Chlamydia is the most prevelant STD. Use of hormonal contraceptives increases your risk of contracting Chlamydia. 75% of women who are infected with Chlamydia do not know they have it, because they have NO SYMPTOMS.
Symptoms of Chlamydia in women include:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Burning sensation with urination
- Lower abdominal pain
- Low back pain
- Painful intercourse
Symptoms of Chlamydia in men include:
- Discharge from the penis
- Burning sensation with urination
- Burning and itching around the opening of the penis
- Symptoms can take 1-3 weeks to appear after exposure
Risks: Increases a woman’s susceptibility to HIV.
If left untreated: Can develop into a “silent” infection, impacting a woman’s future ability to have children.
GONORRHEA
Definition: A sexually transmitted disease caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, a bacterium that can grow and multiply easily in the warm, moist areas of the reproductive tract in women and men. Many women and men have NO SYMPTOMS of Gonorrhea. Symptoms can take up to 30 days to appear.
Symptoms of Gonorrhea in women include:
- Painful or burning sensation when urinating
- Increased vaginal discharge
- Vaginal bleeding between menstrual periods
Symptoms of Gonorrhea in men include:
- Burning sensation when urinating
- White, yellow, or green discharge
Risks: Increases a woman’s susceptibility to HIV. Can be transmitted to infants during birth, causing blindness, joint and blood infections.
If left untreated: Can develop into PID and infertility in both men and women.
BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS (BV)
Symptoms: Can include abnormal vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor, pain, itching or burning.
Risks: Increases a woman’s susceptibility to other STDs.
If left untreated: Can develop into PID, resulting in damage to the fallopian tubes and infertility.
HEPATITIS B
Symptoms: Can include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, clay-colored bowel movements, joint pain, jaundice.
Risks: Can cause jaundice; is easily spread through fecal-oral contact.
If left untreated: Is the leading cause of liver cancer.
HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS
Symptoms: Can include small red bumps or tiny white blisters that become ulcers and can be found on the genitals, buttocks, anus or thighs; sometimes flu-like symptoms.
Risks: Causes recurrent, painful sores and can be transmitted to infants during birth.
If left untreated: Can increase a woman’s chances of contracting HIV.
HIV/AIDS
Symptoms: Can include fatigue, fever, headache, sore throat, rash, swollen lymph glands, diarrhea, dry cough, sudden weight loss.
Risks: Can be symptomless for 10 years or more, but still transmitted to sexual partners or infant during childbirth.
If left untreated: Can progress into AIDS and death.
HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS (HPV)
Symptoms: (image) Can include genital warts, sometimes in the mouth or throat, genital itching or discomfort, bleeding with intercourse.
Risks: Can be spread through contact with the infected area regardless of whether symptoms are present.
If left untreated: Causes genital warts, cervical and vaginal cancers, and rarely, penile and anal cancers.
SYPHILIS
Symptoms: Can include one or more painless, open sores called chancres.
Risks: Can be spread when sores are present anywhere on the body, including the anus and mouth; sores can last 3-6 weeks and leave scars.
If left untreated: Can damage internal organs, resulting in paralysis, blindness, dementia and even death.
TRICHOMONIASIS
Symptoms of Trichomoniasis in Women include:
- discomfort during intercourse and urination
- greenish yellow, possibly frothy discharge
- strong odor
- irritation and itching
Symptoms of Trichomoniasis in Men include:
- discomfort during intercourse and urination
- irritation inside the penis
- mild discharge
- slight burning after urination or ejaculation
Risks: Can increase the probability of acquiring HIV.
If left untreated: Can result in premature or low birth-weight babies.
NOTE: NOTIFY ALL SEX PARTNERS THAT YOU HAVE AN STD SO THEY CAN BE TESTED AND TREATED. YOU SHOULD BE RE-TESTED FOR STDS 3-4 MONTHS AFTER FINISHING TREATMENT.
1. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (2011). “How to prevent sexually transmitted diseases.” FAQ009.
2. Wasserheit JN (1992). Epidemiological synergy: Interrelationships between human immunodeficiency virus infection and other sexually transmitted diseases. Sex Transm Dis, 19(6): 61-77.
3. Forhan SE, Gottlieb SL, Sternberg MR, Xu F, Datta SD, McQuillan GM, et al. (2009). “Prevalence of sexually transmitted infections among female adolescents aged 14 to 19 in the United States.” Pediatrics, 124(6): 1505-12.
